Software as Medical Device: Regulatory-Ready Development
FDA, CE, and international regulatory pathways require specialized expertise. We build SaMD with QMS, risk management, and design controls embedded—not bolted on after.

FDA, CE, and international regulatory pathways require specialized expertise. We build SaMD with QMS, risk management, and design controls embedded—not bolted on after.







Software intended for medical purposes, without being part of a hardware medical device.

Intended for diagnosis, treatment, prevention, or monitoring of disease or medical conditions. The software itself is the medical device.
Diagnosis, treatment, monitoring
Runs on general-purpose computing platforms—mobile devices, web browsers, cloud servers—not dedicated medical hardware.
Mobile, web, cloud
Subject to FDA regulation based on risk classification. May require 510(k), De Novo, or PMA clearance depending on intended use.
510(k), De Novo, PMA
AI-powered screening, image analysis, risk assessment algorithms that aid clinical diagnosis.
Real-time vital sign monitoring, anomaly detection, alert systems for clinical intervention.
Digital therapeutics (DTx) that deliver interventions for conditions like diabetes, mental health, chronic pain.
Health data display, trend analysis, patient education tools that inform but don't diagnose.
Real-time monitoring platform for OR environments with AI-powered anomaly detection, mobile alerts, and device integration—built with SaMD regulatory requirements from day one.
Quality Management System for medical device design and development
Medical device software lifecycle processes

Risk management for medical devices
Usability engineering and human factors
FDA cybersecurity guidance and HIPAA requirements
Performance testing and clinical evidence requirements
Determine risk classification, regulatory pathway, and user needs.
Regulatory strategy + risk class
Define requirements, initiate risk file, establish design controls.
Requirements + risk management file
IEC 62304 compliant development with verification and validation.
Design History File (DHF)
FDA submission support, clearance, and post-market surveillance.
510(k) / De Novo + maintenance
Calendar Year ROI. One team, concept to scale. 75-person integrated team.
10 steps from messy data to measurable outcomes. Most AI projects fail at step 2—we deliver all 10 to production.
$10M+ PDPM recovery. $10M+ RAF improvement. Hard dollar returns within the calendar year.
15 US architects + 60 nearshore delivery. Same timezone, HIPAA-compliant, partners not vendors.

"I have worked with many technology teams during my career, and Digital Scientists is one of the best. They take the time to understand the customers' needs, deliver innovative solutions, are always professional, and work with your team as a true partner to achieve success."
Amy Severino
Chief Innovation Officer, CommuniCare Health Services
Technologies





30-minute call. No pitch. Just honest assessment of what's possible for your organization.
Or call: 404.654.3855
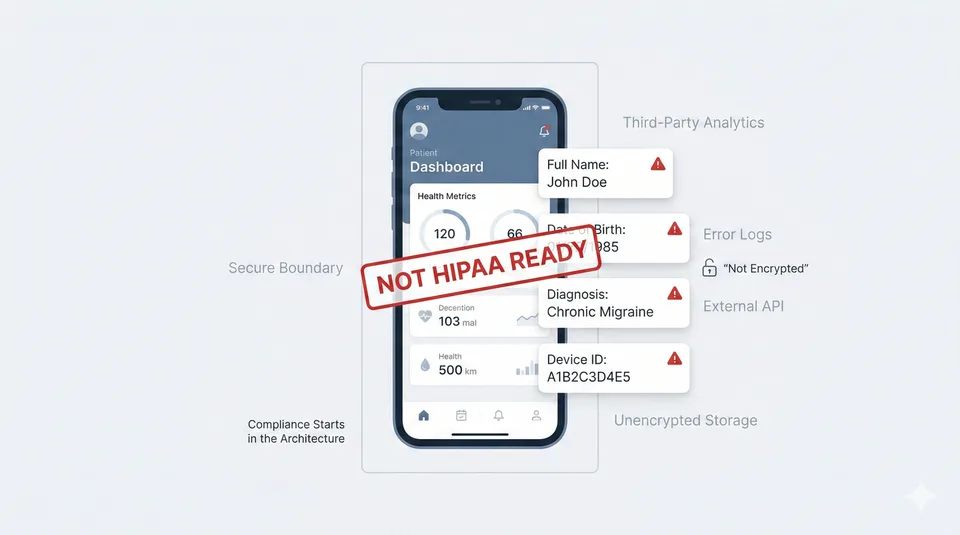
SaMD requires both FDA compliance and data security. We build with HIPAA, FDA cybersecurity guidance, and international requirements (MDR, CE marking) from day one.
Learn more about our compliance approach →
Related Insights

Dec 23, 2025
Feb 03, 2026

Jun 24, 2024