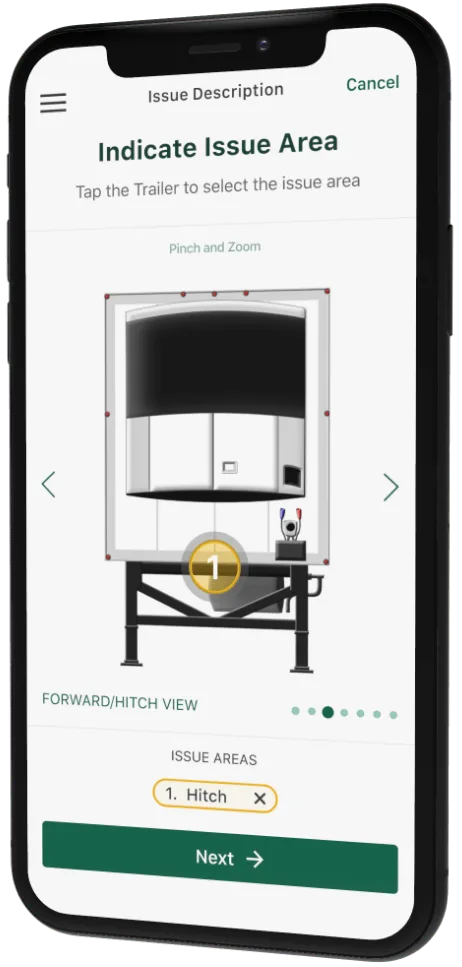
Mobile App Development Services
We build mobile apps that people use every day — to close deals, manage patients, track fleets, and run operations. Since 2008, mobile has been part of nearly every project we ship.
Start a Conversation




200+
Projects delivered
2008
Building mobile apps since
26K+
Patients rely on our apps daily
130+
Facilities running our software
From concept to App Store — and beyond
One integrated team handles product management, UX design, and engineering across every phase. The same people who research your users write the code that ships to the App Store and Google Play.
Discover
Understand the problem, the users, and the constraints. Define what to build and — just as important — what not to build.
Strategy + prioritized features
Phase 2Experiment
Prove the idea works before committing to a full build. Prototype, test with real users, and validate the riskiest assumptions first.
Working prototype + user validation
Phase 3Engineer
Build production-quality mobile software in iterative sprints. Ship to the App Store and Google Play with the infrastructure to scale.
Production app + launch
Phase 4Optimize
Scale based on real usage data. Add features, improve performance, and grow the user base. Mobile is never "done" — it evolves with your business.
Growth + continuous improvement
The most powerful device your team already carries
Your phone is a sensor, a work device, and a universal remote — all in one. We build mobile that connects to Bluetooth, IoT, and the systems around it.
Mobile as a Daily Tool
Apps people open every morning — to check inventory, review patient data, or manage a route. High daily utility is the metric.
Mobile as a Sensor
Camera, GPS, Bluetooth, NFC — your phone collects data no other device can. We connect it to peripherals, wearables, and IoT to turn sensor data into intelligence.
Mobile as a Work Device
Field techs, clinicians, drivers — mobile goes where the work is. We design for offline use, rugged conditions, and one-handed operation.
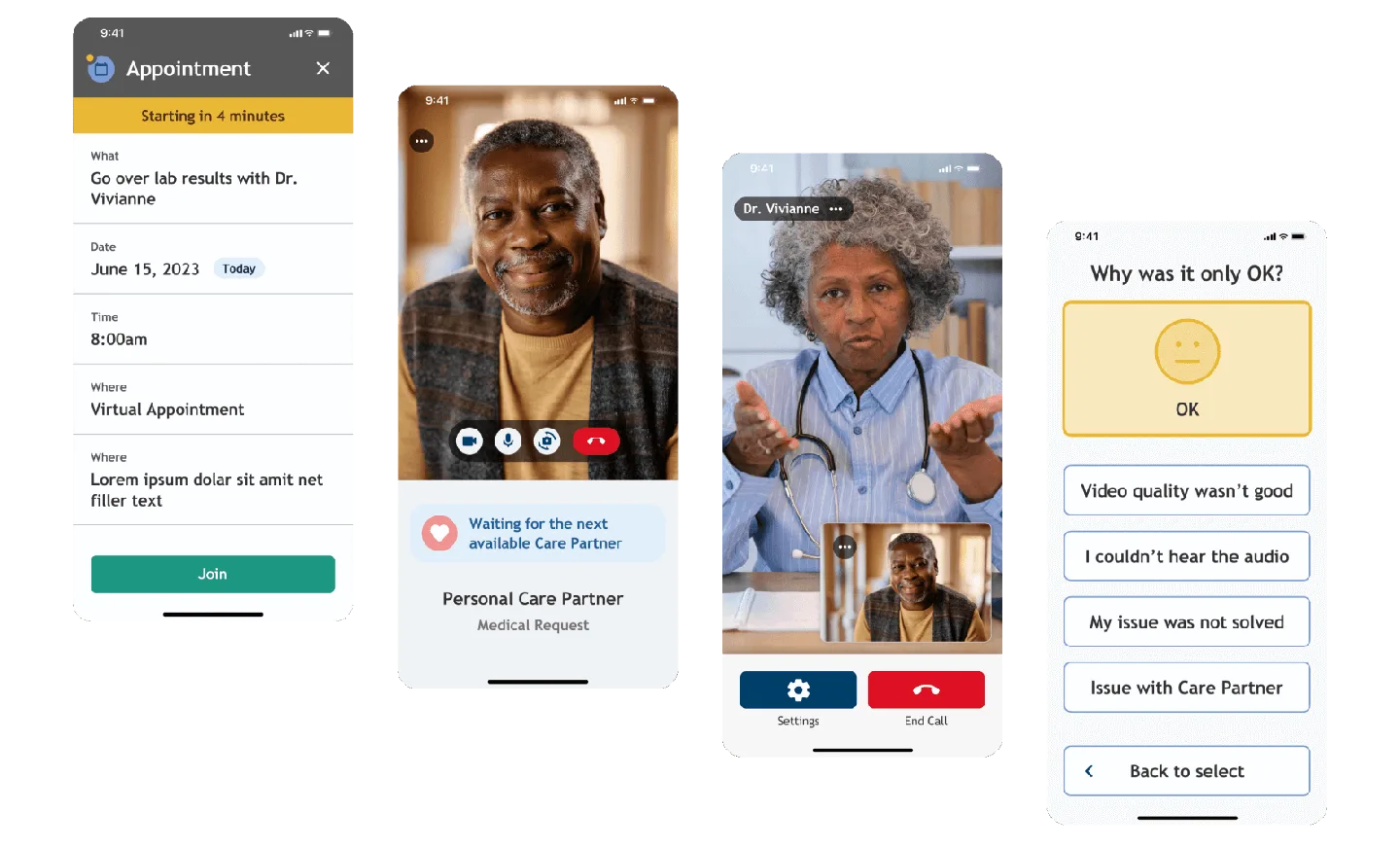
What our clients say

"Our ongoing relationship with Digital Scientists is critical to my efforts at Mailchimp – as we explore new experiences and technologies for our customers. Their team's maturity and ability to deliver while thinking deeply about complex problems helps us gain valuable perspective of what's possible"
CHRIS BEAUREGARD
director of product management, mailchimp

"Digital Scientists helped us drive sales for our KICKR Smart Trainer by developing an innovative and interactive Apple TV app that helps engage and educate our customers. The KICKR experience stations make up some of our most important real estate, but we needed help attracting customers to the stations. The DS team was able to accelerate these efforts and help us truly engage with potential buyers."
TYLER HARRIS
wahooligan product owner

"I have worked with many technology teams during my career, and Digital Scientists is one of the best. They take the time to understand the customers' needs, deliver innovative solutions, are always professional, and work with your team as a true partner to achieve success."
AMY SEVERINO
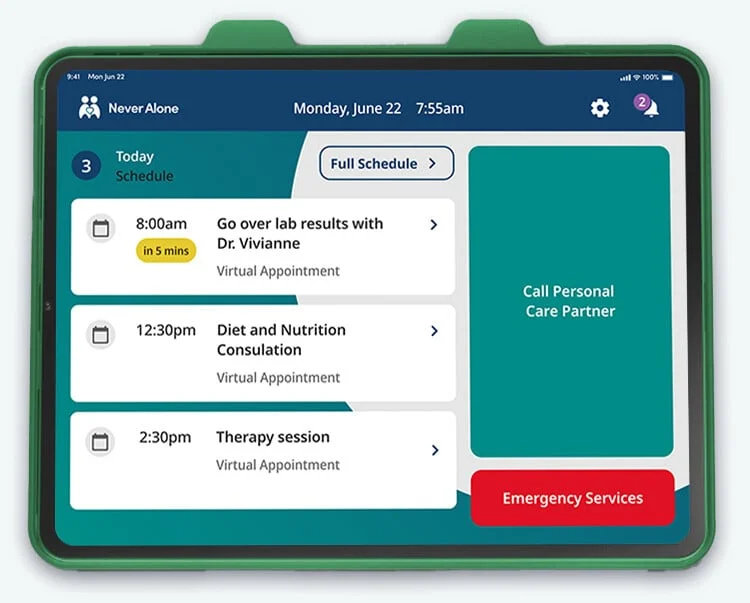
chief innovation officer, NeverAlone (CommuniCare)
Where mobile drives results
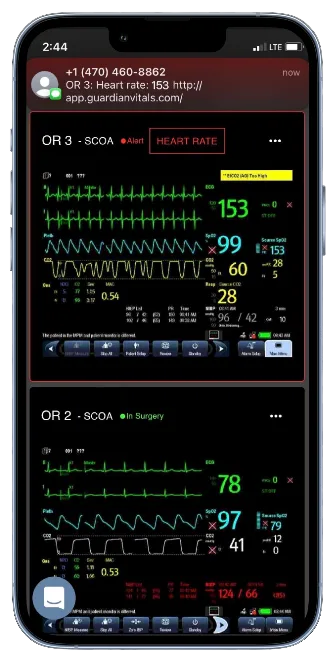
Telemedicine
HIPAA-compliant video visits, secure messaging, EHR integration, and clinical documentation.
Field Sales & Service
Offline-capable CRM tools, route optimization, signature capture, and real-time order entry.
Supply Chain & Logistics
Barcode scanning, inventory tracking, and warehouse management integrated with your ERP.
Fleet & Geolocation
GPS tracking, geofenced alerts, asset monitoring, and battery-efficient background location.
On-Demand Platforms
Consumer app, provider app, and admin dashboard — built as a connected platform that scales.
Marketplace & Commerce
Two-sided platforms with search, payments (Stripe, Apple Pay), reviews, and messaging.
How we work together
Our engagements scale from a one-day session to a full product build. Pick the starting point that fits where you are.
Working Session
Align on goals, constraints, and next steps in a single day.
The Experiment
A working prototype in 5 days that proves whether the idea works.
Blueprint
Full architecture, scope, and a detailed plan before committing to the build.
Full Build
End-to-end mobile app development — design through App Store launch.
Continuous Engineering
Ongoing development, iteration, and scaling after launch.
Production-grade mobile stack
Mobile development thinking

Apple’s App Store Ruling: What Every Mobile Product Owner Needs to Know
How recent changes affect your App Store strategy and what to do about it.
Read More →

8 Practices to Ensure Accessibility in Mobile App Design
Building mobile apps that work for everyone, not just the majority.
Read More →

Sales Enablement Platforms for Your Mobile Sales Force
How mobile tools transform field sales from manual to data-driven.
Read More →
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about mobile app development, cost, and working with Digital Scientists.
Next Step
Ready to See What's Possible?
$20,000. One week. A working prototype that proves whether your idea works — before you commit to a full build.
Since 2007 · 200+ products launched · One team, concept to scale