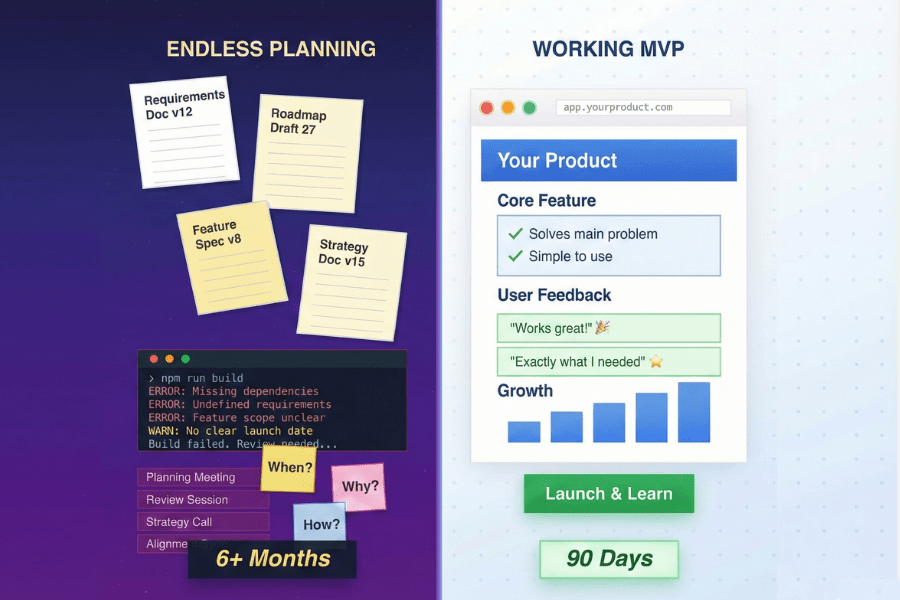
What is accessibility?
Accessibility recognizes that people interact with technology in diverse ways and removes barriers so that people with disabilities can more fully engage with digital content, tools, products, and services.
Statistics and facts about disabilities
People with disabilities are the world’s largest minority
61 million adults in the United States live with a disability
26% of adults in the United
States live with a disability
Over 1 billion people worldwide live with a disability
Almost everyone is likely to experience some form of disability—temporary or permanent, at some point in life.
— Sources: CDC; WHO
Types of disabilities
Physical
Amputation, arthritis, paralysis, repetitive stress injury
Auditory
Hard of hearing, deafness
Visual
Color blindness, low vision, blindness
Speech
Mute, dysarthria (weakness or paralysis of muscles for speech), stutter
Cognitive
Learning, neurological, ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, mental health disabilities (medications may also have side effects), memory impairments, learning disabilities, seizure disorders
Disabilities can be permanent, temporary, or situational


Temporary disabilities
Even a short-term injury or context affects the way people interact with the world around them. Think about a limb injury, ear infection or laryngitis.
Situational disabilities
As people move through different environments, their abilities can also change dramatically. In a loud crowd, they can’t hear well. In a car, they’re distracted. New parents spend much of their day doing tasks one-handed.
Why is accessibility important?
01. Accessibility is part of being inclusive
The web offers valuable resources and services that everyone deserves to access, and that people with disabilities rely on.
“The power of the Web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disability is an essential aspect.”
Tim Berners-Lee ——- W3C Director and inventor of the World Wide Web
02. Accessibility improves the user experience
Essential for some, useful for all. Anyone can experience periods of limitations, or prefer different ways of finding and consuming information. Some benefits are…
- High contrast helps during glare
- Voice recognition helps keep hands free
- Captions help in a loud environment
03. Accessibility drives innovation
Accessibility features in products and services often solve unanticipated problems. Sometimes limitations can propel us to think through problems differently and come up with unique solutions.
04. Accessibility minimizes legal risk
Many countries have laws requiring digital accessibility, and the issue is of increased legal concern. In the United States, there are two main laws governing digital accessibility – the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Section 508.
The ADA is a law that protects people with disabilities in many areas of public life. Title II applies to web accessibility for State and local governments. Title III applies to businesses that are open to the public.
Section 508 establishes accessibility requirements for electronic and information technology developed, maintained, funded, or used by the Federal Government.
05. Clients may require accessibility
In addition to client requirements, every federal agency or any organization that interacts with a federal agency is required to complete a legally binding Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT)—it details a product’s level of conformance with International Web Accessibility Content Guidelines (WCAG).
“By 2025, all G20 countries – which account for 90% of the global world product – will establish enforceable legal standards for digital accessibility, leading to a “GDPR moment” in which businesses scramble to achieve compliance.”
GARTNER REPORT
06. Accessibility adds value
Some clients may not realize the importance or value of accessibility. This gives us an opportunity to establish the value of our contributions to the success of their product. It may also give us a marketing edge against competing agencies.
Although accessibility adds some additional effort, it will be a much larger effort to have to go back and fix a product.
07. Accessibility may affect your reputation and marketability
Diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts are important to business success and reputation. People may prefer to support companies who share their values and who design products that fit their needs.
“By 2023, digital products in full WCAG Level 2 compliance will outperform their market competitors by 50%.”
GARTNER REPORT
08. Accessibility positively affects SEO
There’s a considerable overlap between features that improve accessibility and SEO performance.
- Metadata
- Image Alt text
- Link anchor text
- Heading tag structure
- Audio and video transcriptions
How people with disabilities access digital content
People with disabilities use assistive technologies or adaptive techniques to access digital content. In order to use these successfully, they rely on content that has been designed and coded following accessibility standards, and that has been tested.

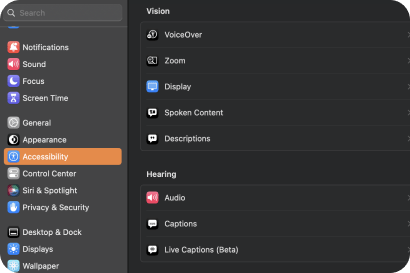
Assistive technologies
Software and hardware that people with disabilities use to improve interaction with the web. Some examples are:
+ Alternative keyboard or mouse
+ Refreshable braille display
+ Screen magnifier
+ Screen reader
+ Voice recognition software
Adaptive techniques
Techniques to improve interaction with the Web. These include techniques with standard software or mainstream web browsers, such as the following:
+ Increasing text size
+ Turning on captions
+ Reducing motion
+ Voice control
+ Pointer control
We’re committed to creating products that everyone can use
As the world’s largest minority, people with disabilities deserve to access digital content. Understanding and incorporating accessibility guidelines can be a complex process. Research and testing takes time. However, it’s not just about checking off boxes to mitigate legal liabilities, it’s about doing the right thing and ensuring everyone can access digital content, tools, products, and services.
As we continue to design, build, and learn, we promise to work hard to understand the needs of people with disabilities, for the best user experience possible.